Edge Computing in Industry: Benefits and Applications
March 28, 2025

1. What is Edge Computing?
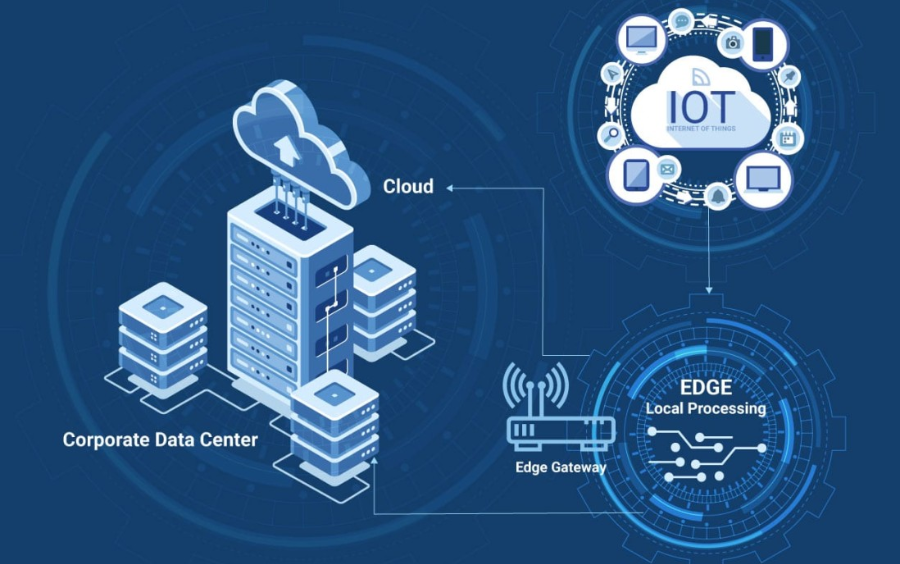
Edge Computing is a data processing model that processes data at the source instead of sending it entirely to the cloud. This reduces latency, saves bandwidth, and enhances security. In industrial environments, where automation systems require fast and stable responses, Edge Computing plays a crucial role in optimizing operations.

1.1. The Difference Between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing: Data is sent to remote servers for processing before returning results.
- Edge Computing: Data is processed directly at the device or edge nodes, enabling faster responses.
- Hybrid Edge-Cloud Approach: Some systems leverage both methods to optimize performance and costs.
2. Benefits of Edge Computing in IoT
2.1. Reduced Latency
- On-site data processing enables faster response times, significantly lowering latency compared to cloud computing.
- Applications include industrial AI, machine monitoring, and production line control.
- Automation systems require low latency to ensure smooth operation, such as industrial robots and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
2.2. Bandwidth Savings
- Reduces data transmission to the cloud, easing network load.
- Only critical data is sent to the cloud for in-depth analysis.
- Lowers transmission costs, especially in systems with millions of IoT sensors.
2.3. Enhanced Security
- Limits the risk of data breaches as processing occurs locally.
- Critical systems like SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) require high security to prevent external attacks.
- Enables direct implementation of data encryption and device authentication at the edge.
2.4. Operational Stability
- Systems continue to function even when internet connectivity is lost.
- Ensures uninterrupted industrial production and operations.
- Essential for 24/7 manufacturing systems that cannot afford downtime.
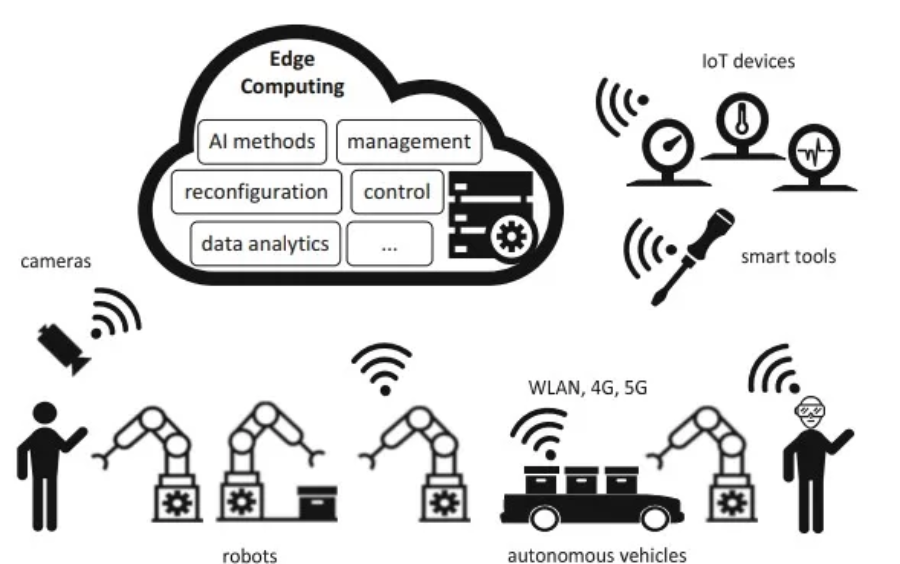
3. Applications of Edge Computing in Industry
3.1. Smart Factories
- Production line monitoring to detect errors early.
- Controlling industrial robots with low latency.
- Energy management to optimize power consumption in factories.
3.2. Mining and Oil & Gas
- Monitoring machinery performance in harsh environments.
- Early warning systems to prevent explosions or major failures.
- Vibration and temperature analysis for predictive maintenance.
3.3. Logistics & Transportation
- Efficient supply chain management, real-time tracking of goods.
- Warehouse temperature monitoring to ensure optimal storage conditions.
- AI-powered route optimization, reducing fuel costs.

4. The Future of IIoT with Edge Computing
4.1. Integration of AI, 5G, and Edge Computing
- 5G enables faster data transmission, supporting ultra-low-latency applications.
- AI and Edge Computing work together to process data intelligently at the network edge.
- Blockchain integration enhances security and transparency in industrial IoT systems.
4.2. Trends in Edge Computing for Industry
- Businesses shifting from Cloud-first to Edge-first to enhance efficiency.
- New cybersecurity standards to mitigate security risks.
- Virtualized networks and SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) make managing distributed IoT systems easier.